
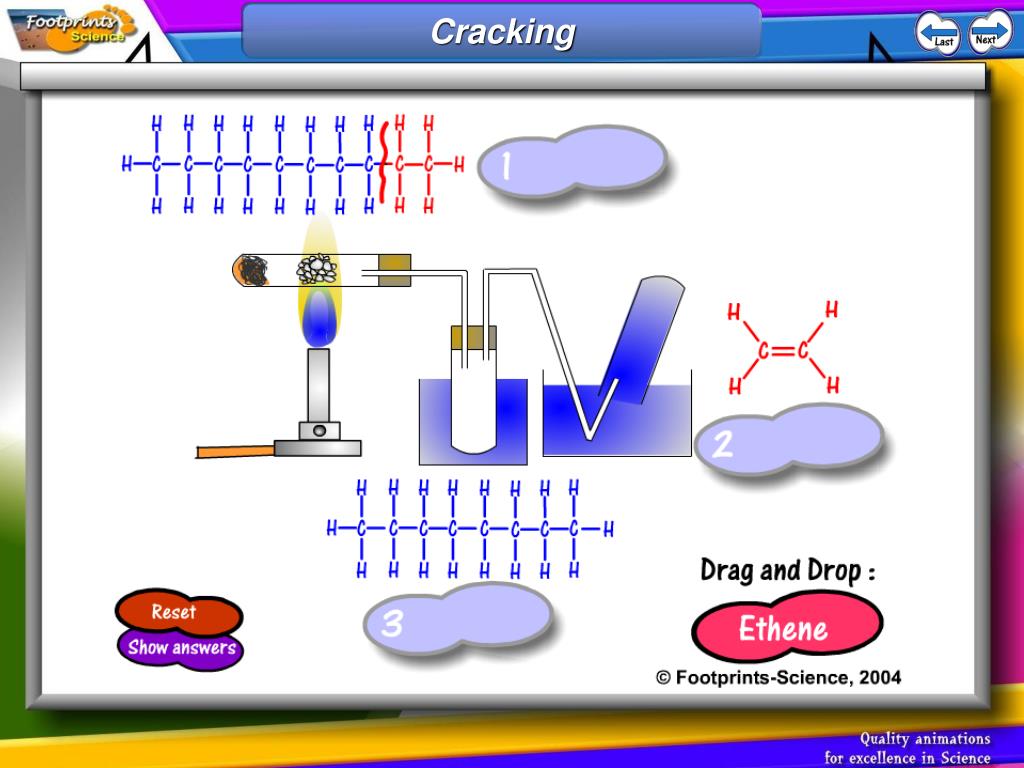
The alkenes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons because they all contain at least one carboncarbon double bond.

The simplest alkenes have the general formula C nH 2n. Ethene (C 2H 4) is an example of a family of hydrocarbons called the alkenes. One of the by-products of this thermal decomposition reaction is ethene. Cracking takes place at high temperatures as the large molecules pass over a catalyst. Summary Oil companies break large hydrocabon molecules down into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons. They are less likely to clog up your arteries with the fatty deposits that can cause heart disease.

They are a healthier option than the saturated fats we eat in butter. Some of them are called polyunsaturates because their molecules have more than one double bond. Have you heard of the unsaturated oils we use to make margarine? These contain double bonds in their carbon chains too.
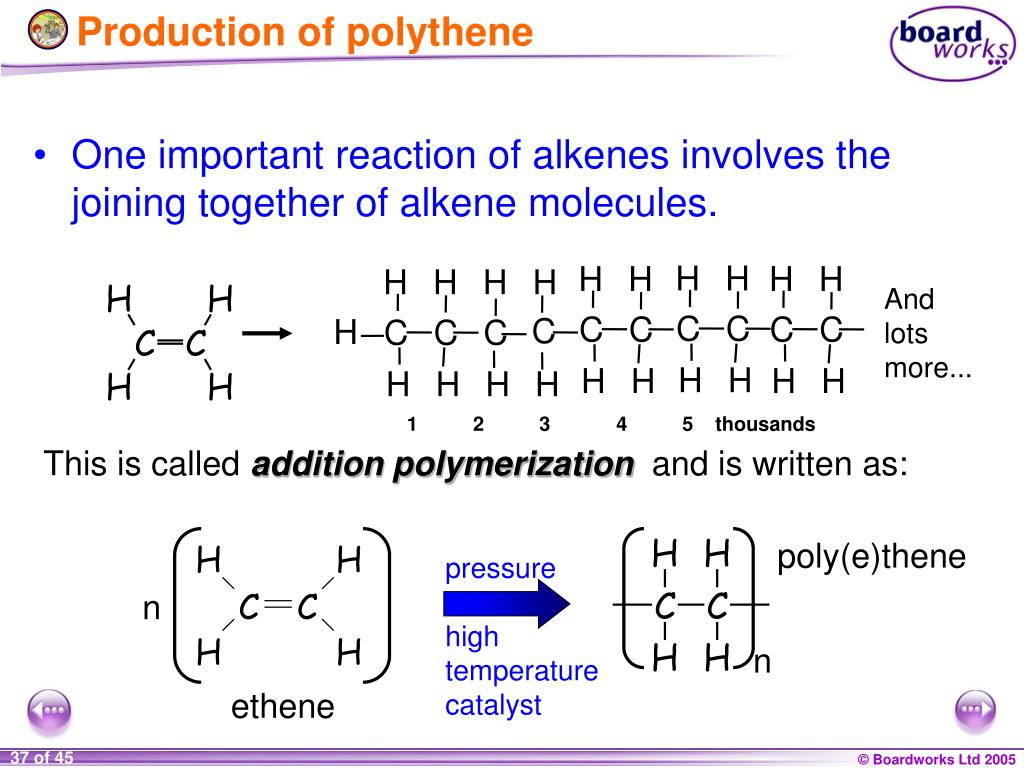
So while the alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, the alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. When all the carboncarbon bonds are single, a molecule is said to be saturated. Atom such as hydrogen added to each carbon atom. Let's look at the structures of the first three members of the alkenes, shown in Fig.2 below.ĪtomAn atom is the smallest particle of an element that can still be defined as that element. Its name is ethene and it is the smallest member of the family of hydrocarbons called the alkenes. So the small molecule C 2H 4 is not an alkane. Here's the equation again: C 10H 22(g) C 8H 18(g) + C 2H 4(g) Remember that the general formula for an alkane is C nH (2n+2). Molecule formed in the equation given for cracking in the previous section? MoleculeA molecule is a group of two or more atoms bonded together. (A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction but remains chemically unchanged itself at the end of the reaction.) Look at an example of cracking below: C 10H 22(g) C 8H 18(g) + C 2H 4(g) Cracking is an example of a thermal decomposition reaction (in this case of an. Catalyst, and they break down into smaller molecules. CatalystA catalyst is a substance that alters (usually speeds up) the rate of a chemical reaction, but remains chemically unchanged itself at the end of the reaction. But we just don't use so much of the heavier fractions, so chemists have found ways to meet the demand for petrol by producing this from the heavier hydrocarbons. The fractions that provide us with fuel for cars are in great demand. As you might expect, we do not need as much of some fractions as others. It is the raw material for many fuels and plastics. Crude oilCrude oil is a liquid formed from tiny sea creatures and plants that died millions of years ago.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
